With this theories part is completed.
6)
USES AND GRATIFICATION THEORY
This theory propounded
by Katz in 1970, is concerned with how people use media for
gratification of their needs. An outcome of Abraham
Maslow's Heirarchy of Needs, it propounds the fact that people
choose what they want to see or read and the different media compete to satisfy
each individual"s needs.
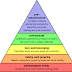
In the hierarchy of needs, there are five levels
in the form of a pyramid with the basic needs such as food and clothing at the
base and the higher order needs climbing up the pyramid. The fulfillment of each lower level need leads to the
individual looking to satisfy the next level of need and so on till he reaches
the superior-most need of self-actualization.
Figure
2.2
The
Uses and Gratifications approach reminds us that people use media for many purposes. As media users become increasingly confronted with
choices, this approach should direct our attention to the audience. Lull's television research found that families used
television for communication facilitation, relationship building, intimacy, and
for structuring the day. In general researchers have found four kinds of
gratifications:
1. Information - we want to find out
about society and the world- we want to satisfy our curiosity. This would fit
the news and documentaries which both give us a sense that we are learning
about the world.
2. Personal Identity - we may watch the television in order to look for models for our behaviour. So, for example, we may identify with characters that we see in a soap. The characters help us to decide what feel about ourselves and if we agree with their actions and they succeed we feel better about ourselves.
3. Integration and Social Interaction - we use the media in order to find out more about the circumstances of other people. Watching a show helps us to empathize and sympathize with the lives of others so that we may even end up thinking of the characters in programme as friends.
4. Entertainment - sometimes we simply use the media for enjoyment, relaxation or just to fill time.
Riley and Riley (1951) found that children in peer groups used
adventure stories from the media for group games while individual children used
media stories for fantasizing and daydreaming. The study thus found that
different people use the same messages from the media for different purposes.
Katz replaced the question "what do media do to
people?" with the question "what do people do with the media?" Katz,
Gurevitch & Hass found that the media are used by
individuals to meet the following specific needs :
individuals to meet the following specific needs :
1) Diversion (emotional release)
2) Personal Relationships (substitute of media for companionship).
3) Personal identity or individual psychology (value reinforcement, self understanding.)
4) Surveillance (information that may help an individual accomplish tasks.)
2) Personal Relationships (substitute of media for companionship).
3) Personal identity or individual psychology (value reinforcement, self understanding.)
4) Surveillance (information that may help an individual accomplish tasks.)
B. Rubin and Bantz (1989) studied the uses and gratifications of
"new technology" by examining VCR use. They
found the following motives for VCR use:
1) library storage of movies and shows
2) watching music videos
3) Using exercise tapes
4) renting movies
5) letting children view
6) time-shifting
7) Socializing by viewing with others
8) Critical viewing including TV watching and studying tapes
Propounded by Elisabeth Noelle-Neumann, this
theory states that the media publicizes opinions that are mainstream and people
adjust their opinions according to their perceptions to avoid being isolated. Individuals who perceive their own opinion as being
accepted will express it, whilst those who think themselves as being a
minority, suppress their views. Innovators and change agents are unafraid to
voice different opinions, as they do not fear isolation.
Figure
2.3
Festinger formulated the consistency theories that talked
about people"s need for consistency in their beliefs and judgements. In order to reduce dissonance created by
inconsistencies in belief, judgments and action people expose themselves to
information that is consistent with their ideas and actions, and they shut out
other communications.
This theory puts forth the ability of the media to influence the significance of events in the public's mind. The media set the agenda for the audience's discussion and mentally order and organize their world. The theory is consistent with a "use and gratification" approach.
McCombs and Shaw
assert that the agenda-setting function of the media causes the correlation
between the media and public ordering of priorities. The
people most affected by the media agenda are those who have a high need for
orientation
Developed by Ball-Rokeach and DeFluer, the key idea behind this theory is that audiences depend on media information to meet needs and reach goals, and social institutions and media systems interact with audiences to create needs, interests, and motives in the person. The degree of dependence is influenced by the number and centrality of information functions and social stability.
Some questions
that this theory raised were :
Do media create needs?
Do people turn to media to achieve gratification and satisfy needs?
Are media needs personal, social, cultural, political, or all of these?
"The media are our friends"??
Do media create needs?
Do people turn to media to achieve gratification and satisfy needs?
Are media needs personal, social, cultural, political, or all of these?
"The media are our friends"??
11)
STEPHENSON"S PLAY THEORY
Play is an activity pursued for pleasure. The
daily withdrawal of people into the mass media in their after hours is a matter
of subjectivity. The effect of mass communication
is not escapism nor seducing the masses. Rather it is seen as anti-anxiety
producing, and are regarded as communication-pleasure.
Behaviors which are modeled from media
experiences can become habitual if found useful and/or if they are reinforced
in the environment. This is not about violent or criminal behavior.
These theories suggest that mediated experiences induce long term effects that are very difficult to measure. The effects are like stalagmite drippings building up over time. Meaning Theory and the Cultivation Theory are two of the most significant Stalagmite theories.
Media experiences mould meanings by putting things in a particular framework. Does "NYPD Blue" depict the real world of New York City police detectives? Questions like this are coming from a Meaning Theory focus on media.
George Gerbner tried to determine the influence of television on viewers" ideas of the environment they lived in. He found that dominance of TV created a common view of the world and that it homogenized different cultures. TV portrayed the society as a bad place to live in leading to people becoming distrustful of the world. Over time, particular symbols, images, messages, meanings become dominant and are absorbed as the truth. Cultural stereotypes, ways of assessing value and hierarchies are established.
Figure
2.4
Pioneered in 1943 by Bryce Ryan and Neil Gross of Iowa State University this theory traces the process by which a new idea or practice is communicated through certain channels over time among members of a social system. The model describes the factors that influence people's thoughts and actions and the process of adopting a new technology or idea.
15)
Social learning theory
Formulated by Albert Bandura at Stanford University, this specifies that mass-media messages give audience members an opportunity to identify with attractive characters that demonstrate behavior, engage emotions, and allow mental rehearsal and modeling of new behavior. The behavior of models in the mass media also offers vicarious reinforcement to motivate audience members' adoption of the behavior.
1. microscopic theories that focus on the everyday life of people who process information - for example, uses and gratifications, active audience theory, and reception studies;
2. middle range theories that support the limited effects perspective of the media - for example, information flow theory, diffusion theory, and
3. macroscopic theories that are concerned with media's impact on culture and society - for example, cultural studies theory.
Theories of mass communication have always
focused on the "cause and effects" notion, i.e. the effects of the
media and the process leading to those effects, on the audience's mind.
Harold Lasswell and Berelson have
succinctly expressed this idea. Lasswell's
essential question is timeless (1949): "Who says what in what channel
to whom with what effects?" Berelson said:
"Some kinds of communication, on some kinds of issues, brought to the
attention of some kinds of people, under some kinds of conditions, have some
kinds of effects." (1949).
Figure
2.5
Wilbur Schramm stated: "In fact, it is misleading to
think of the communication process as starting somewhere and ending somewhere.
It is really endless. We are little switchboard centers handling and rerouting
the great endless current of information.... " (Schramm W.1954) quoted
in McQuail & Windahl (1981)
16)
The Osgood and Schramm circular model emphasizes the circular nature of
communication.
The
participants swap between the roles of source/encoder and receiver/decoder.
Figure
2.6
17)
Gerbner's General Model
Gerbner's
General Model also emphasizes the dynamic nature of human communication.
Figure
2.7
Shannon and Weaver
produced a general model of communication known after them as the
Shannon-Weaver Model. It involved breaking down
an information system into sub-systems so as to evaluate the efficiency of
various communication channels and codes. They propose
that all communication must include six elements:
This model is often
referred to as an " information model" of communication. A drawback is that the model looks at communication
as a one-way process. That is remedied by the
addition of the feedback loop. Noise indicates
those factors that disturb or otherwise influence messages as they are being
transmitted
Berlo"s SMCR (SOURCE, MESSAGE, CHANNEL, and
RECEIVER) model focuses on the individual characteristics of communication and
stresses the role of the relationship between the source and the receiver as an
important variable in the communication process. The
more highly developed the communication skills of the source and the receiver,
the more effectively the message will be encoded and decoded.
Berlo's model represents a communication process that
occurs as a SOURCE drafts messages based on one's communication skills,
attitudes, knowledge, and social and cultural system. These MESSAGES are transmitted along CHANNELS, which
can include sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. A RECEIVER interprets
messages based on the individual's communication skills, attitudes, knowledge,
and social and cultural system. The limitations of the model are its lack of
feedback
Terms
used in the chapter:
It is a collective phrase that represents not only the press, cinema, radio, television and internet, but also to some extent, books magazines, pamphlets , direct mail literature, posters, folk media, and natural communication methods such as rumours, education and preaching. It is so termed because its reach extends to vast heterogeneous populations. Generally the mass media employ technological means to communicate to the masses. They are founded on the idea of mass production and distribution. Wiebe defined mass media as those readily available to the general public.
The media are full of competing messages. The process of screening vast amount of information in which one has no interest through mental filters is called selective attention, for example, an adult will be more tuned to listening to the news while a child would rather watch a cartoon show.
This is the tendency to interpret communication messages in terms of one"s
existing attitudes. People of distinct psychological character same media
content in different ways. This depends on factors such as age, values, family,
opinions etc. Selective perception is influenced by social relationships.
The ability of an individual to retain certain messages in his mind while ignoring others is called selective retention. This is influenced by various psychological and physiological factors such as choice, values, culture, emotions etc.
Some individuals are exposed to certain media effects/messages while some are not. This screening aspect depends on many factors such as reach of media, accessibility, age, cultural acceptability, taboos, etc.
The opinions of people in a group are influenced by what they hear from "opinion leaders". An individual who is a member of a group manifests certain characteristics in his thinking and behaviour that contribute to the formation of "public opinion". The opinion of the leader is based on rational thinking due to education and experience. They weigh the pros and cons of the information they receive and then give their judgement on it.
In the process of communication, the sender or source of the message is referred to as the encoder.
The person receiving the message and decodes it is referred to as the decoder.
Feedback, a term form cybernetics, the study of messages. It refers to an inquiry, response or experiment. Feedback can be positive (when the required result is achieved) or negative; instantaneous(when the response is immediate) or delayed. Feedback is used to gauge the effectiveness of a particular message put forth or situation that has taken place.
In all communication, there is a sender, a message/communication and a receiver. The meaning of a message is greatly dependent on the culture in which it is transmitted. The sender encodes a message, the receiver decodes it. Between the sender, the message and receiver, noise gets in the way and complicates the process. A noiseless communication does not exist. There always is some kind of noise entering the communication.
Noise can be physical noise
for example static or psychological i.e. when culture, taboos or values come
into play to disrupt the normal transmission process of communication.
Misunderstanding of a particular message i.e. distortion of meaning is a form
of noise, example, the game of Chinese Whisper"a person starts off with a
particular message and the original message may be distorted by the time it
comes to the final player.
@ Vishiwjeet Singh
Under Creative Commons License